Telefonica, a major telecommunications company, recently confirmed a breach in their internal ticketing system, which led to a significant data leak. The breach involved unauthorized access and extraction of sensitive information, including a vast amount of employee and operational data.
Introduction to Malware Binary Triage (IMBT) Course
Looking to level up your skills? Get 10% off using coupon code: MWNEWS10 for any flavor.
Enroll Now and Save 10%: Coupon Code MWNEWS10
Note: Affiliate link – your enrollment helps support this platform at no extra cost to you.

Infostealer Malware and Social Engineering Tactics
New information has emerged indicating that the breach was facilitated by a combination of infostealer malware and sophisticated social engineering techniques.
Hudson Rock researchers spoke to the threat actors involved in the hack, and according to them, private infostealer malware was used to compromise over 15 employees. This provided the attackers with critical credentials, enabling them to gain initial access.
 Conversation with threat actor Pryx
Conversation with threat actor PryxThe initial access was obtained through https://jira.globalsap.telefonica.com. While Hudson Rock did not have the specific credentials for this access, we identified 10 Telefonica employees in 2024 alone who were infected by Infostealers and had credentials granting access to the same Jira platform.
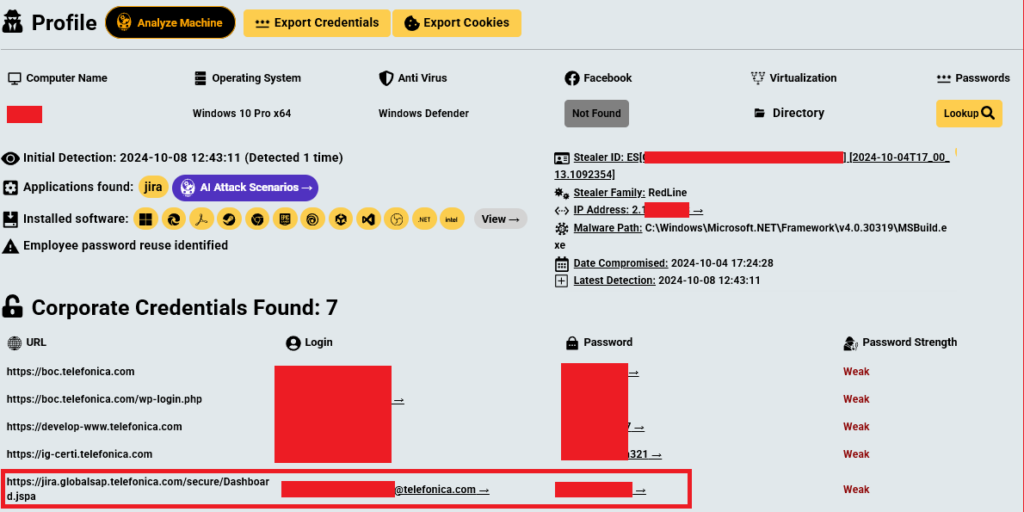 Similar access to the one used by Hellcat group found in compromised Telefonica employees’ computers
Similar access to the one used by Hellcat group found in compromised Telefonica employees’ computersOnce inside, the attackers, part of the Hellcat group, strategically used social engineering to expand their access. Notably, they targeted two employees with administrative privileges, tricking them into revealing the correct server for brute-forcing SSH access. This multi-faceted approach highlights the evolving complexity of cyber threats.
 Jira ticket submitted via a compromised Telefonica employee, it reads: “I am writing to report an issue I am encountering when trying to access the server 190.237.119.41 via SSH using my current credentials. Despite using the correct server address, I receive an unexpected error message.”
Jira ticket submitted via a compromised Telefonica employee, it reads: “I am writing to report an issue I am encountering when trying to access the server 190.237.119.41 via SSH using my current credentials. Despite using the correct server address, I receive an unexpected error message.”
Details on the Stolen Data
The attackers managed to scrape and exfiltrate extensive internal data. Key details include:
- 24,000 Employee Emails and Names: The list contains emails and names of Telefonica employees, potentially exposing them to further phishing and impersonation risks.

- 500,000 JIRA Issues and Summaries: The data includes summaries of internal JIRA issues, which can reveal sensitive operational details, project plans, and vulnerabilities within Telefonica’s infrastructure. This poses a significant risk as it could be used to map out internal workflows and exploit weaknesses.

- 5,000 Internal Documents: The breach also resulted in the theft of internal email communications and various documents. These documents likely contain confidential information, strategic plans, and internal communications, further compromising Telefonica’s operational security.


Broader Infostealer Problem
The breach was essentially imminent. In 2024 alone, Hudson Rock identified that Telefonica had a staggering 531 employee computers infected by infostealers, meaning 531 different employees downloaded and executed infostealing malware. Each infection led to corporate credentials being stolen from their computers and falling into the hands of hackers.
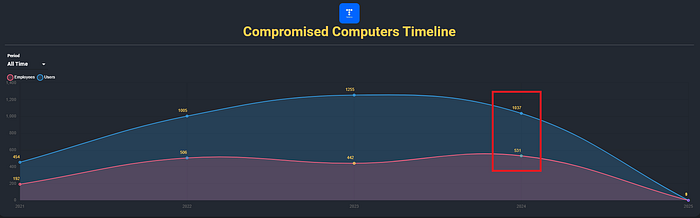
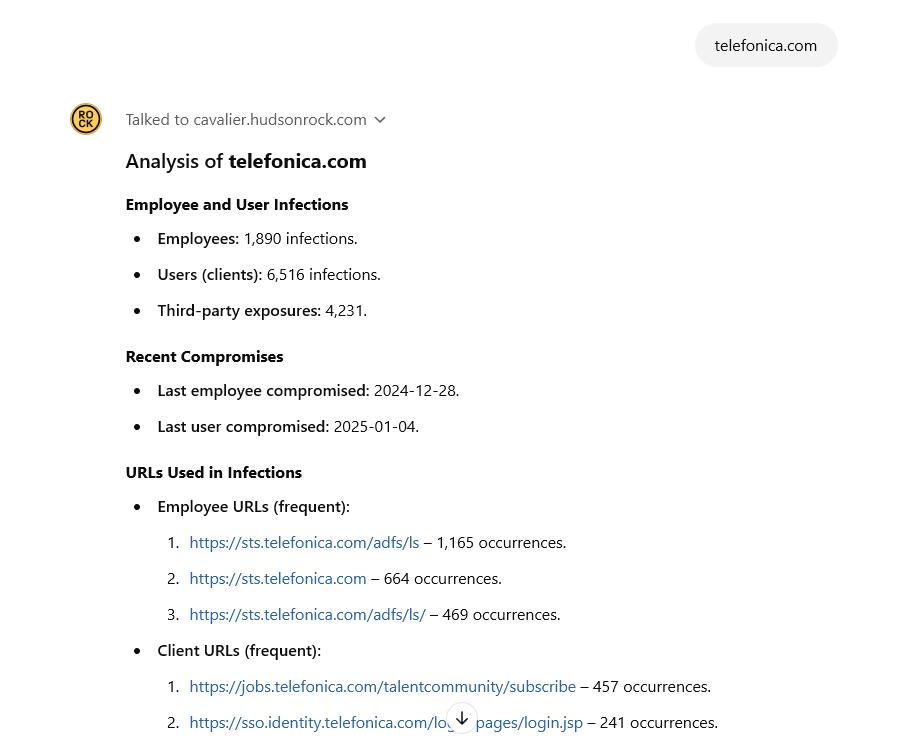 Information via CavalierGPT which contains information about over 30,000,000 computers infected by infostealers – www.hudsonrock.com/cavaliergpt
Information via CavalierGPT which contains information about over 30,000,000 computers infected by infostealers – www.hudsonrock.com/cavaliergptOut of the broader 1890 total employee infections at Telefonica, employees primarily had credentials associated with Active Directory access to Telefonica’s cloud services, intranet logins, and webmail accounts.

When examining the overall password strength of employees via Hudson Rock’s cybercrime intelligence database, it is notable that Telefonica did not enforce strong password requirements for corporate infrastructure. Approximately 66% of the passwords found were considered weak (6–8 characters with only 2–3 types of characters).

Specifically, for the URL linked to the initial access, the passwords were even weaker, indicating that it wouldn’t have taken an infostealer infection for hackers to brute force their way in.

In addition to this significant cyber hygiene issue, Telefonica also had 4,200 instances of employees infected by infostealers who had corporate logins to third-party systems (e.g., Office365, Salesforce, Fortinet, and others).
 Third party credentials which are commonly found on infected computers belonging to Telefonica employees
Third party credentials which are commonly found on infected computers belonging to Telefonica employeesConclusion
The Telefonica breach highlights the growing threat posed by infostealer malware, which continues to be a primary method of gaining initial access to corporate networks.
These infections provide hackers with the necessary credentials to infiltrate systems and, as demonstrated in this case, can be leveraged to expand access further through sophisticated social engineering tactics. Infostealers serve as a stepping stone for more advanced attacks, making them a significant concern for organizations worldwide.
The fact that over 500 employees were compromised is a testament to how widespread these infections can be, and they underscore the need for enhanced security protocols, including better credential management, employee awareness, and robust malware defenses.
To learn more about how Hudson Rock protects companies from imminent intrusions caused by info-stealer infections of employees, partners, and users, as well as how we enrich existing cybersecurity solutions with our cybercrime intelligence API, please schedule a call with us, here: https://www.hudsonrock.com/schedule-demo
We also provide access to various free cybercrime intelligence tools that you can find here: www.hudsonrock.com/free-tools
Thanks for reading, Rock Hudson Rock!
Follow us on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/hudson-rock
Follow us on Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/RockHudsonRock
The post Telefonica Breach: Infostealer Malware Opens Door for Social Engineering Tactics appeared first on InfoStealers.
Article Link: Telefonica Breach: Infostealer Malware Opens Door for Social Engineering Tactics | InfoStealers
1 post - 1 participant
Malware Analysis, News and Indicators - Latest topics


Post a Comment
Post a Comment