Overview of the Snowflake Breach: Threat Actor Offers Data of Cloud Company’s Customers
In recent weeks, Snowflake, a leading cloud-based data storage and analytics provider, has found itself at the center of a cybersecurity controversy. Reports of the Snowflake breach have emerged suggesting unauthorized access to its systems, which may have compromised sensitive data belonging to multiple high-profile clients, including Santander Bank and Ticketmaster.

Snowflake is a cloud-based data platform that facilitates data storage, processing, and analytics, offering essential tools for data-driven applications.
This blog post will detail the Snowflake breach, based on disclosures from Snowflake, news reports, and additional information from cybersecurity researchers.
The Background of the Snowflake Breach and Initial Disclosure
Snowflake noticed unusual activity within its systems around mid-April 2024 and officially acknowledged potential unauthorized access on May 23, 2024. Since then, the company has been actively investigating the situation and has communicated with affected customers, providing them with Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) and recommended actions to secure their accounts.
Despite allegations of a widespread breach, Snowflake maintains that the incidents resulted from compromised user credentials rather than any inherent vulnerabilities or flaws within Snowflake’s product itself.
The company emphasized in a disclosure on Snowflake Forums, published a month ago, that the breach was not due to any misconfiguration or malicious activities within Snowflake’s products, and that customers are recommended to review their security configurations.
How Did the Snowflake Breach Occur?
Investigations reveal that the breach was likely facilitated by a compromised machine used by a Snowflake sales engineer. This suggests that the breach could potentially involve prospect and sales-related environments and production accounts.
The machine was reportedly infected with Lumma Stealer, a type of malware that logs keystrokes and other activities, which could have been the attackers’ initial access point.
The threat actor responsible for the breach claimed to have extracted sensitive data from major entities like Santander Bank and Ticketmaster.
Shortly after, Santander Bank acknowledged that attackers accessed a database hosted by a third-party provider. While they did not explicitly name Snowflake, subsequent revelations linked the breach to Snowflake’s compromised environments.
Similarly, Ticketmaster’s parent company, Live Nation Entertainment, confirmed unauthorized activity in a third-party cloud database environment containing data primarily from Ticketmaster. This breach was also later attributed to Snowflake’s platform.
Following the breach, several cybersecurity firms conducted detailed analyses to understand the scope and impact.
Reports indicated that over 500 demo environment instances were detected in the stealer logs linked to the compromised Snowflake account.
Also importantly, security researcher Kevin Beaumont noted on Mastodon that six major organizations have experienced cybersecurity issues related to their use of Snowflake, indicating a broader impact.
Who Is Behind the Snowflake Breach?
A significant figure in this incident is a threat actor known by the alias “Whitewarlock.” This threat actor first appeared on a Russian dark web forum, Exploit.in, on May 23, 2024, the same day they posted data allegedly obtained from the breach. The data, purportedly belonging to Santander Group, included customers’ data, account numbers and balances, credit card numbers, and HR employee lists, among other information.
The threat actor claimed responsibility for the breach and expressed a desire to sell back the stolen data to Snowflake for $2 million.
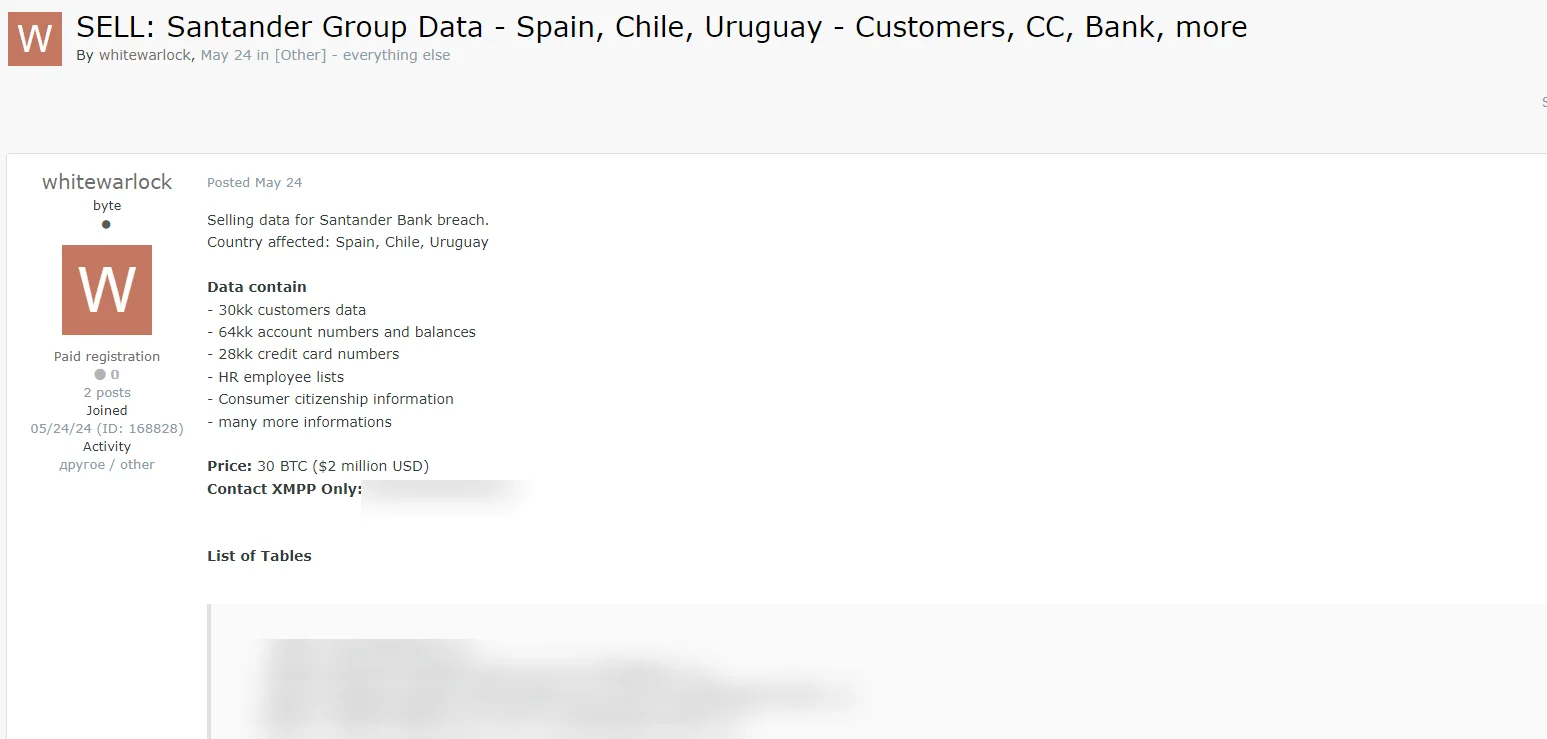
Santander Group data breach post by the Whitewarlock threat actor
ShinyHunters, whose reputation was damaged after the law enforcement operation, shared the same data to attract attention, while also further promoting the Snowflake breach.
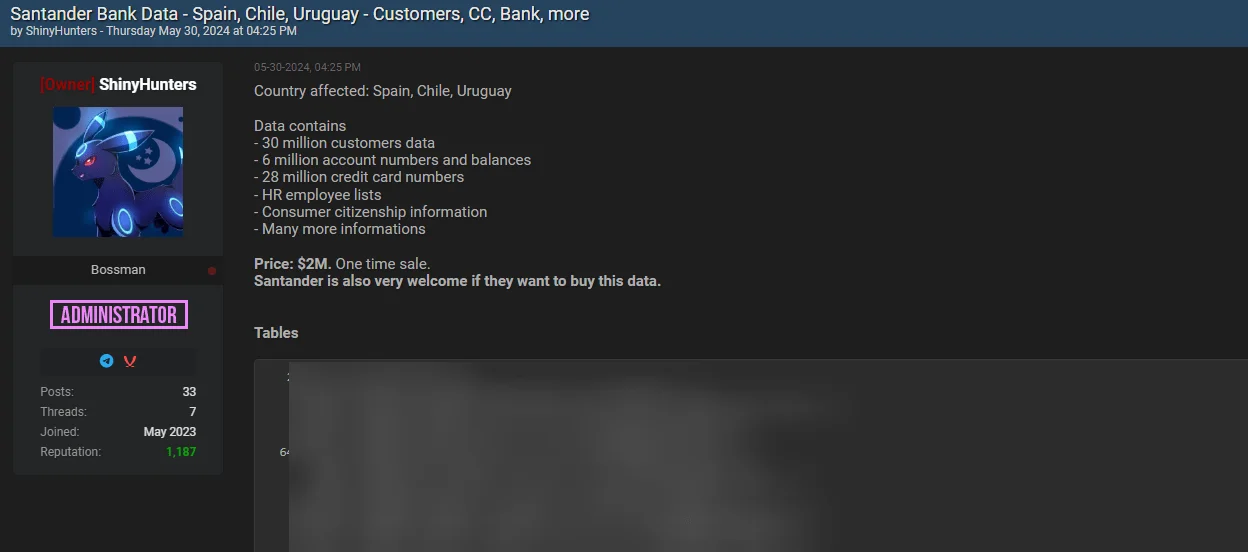
Santander Bank data breach post by ShinyHunters
Whitewarlock’s activities and reputation within the cybersecurity community remain unclear, with no prior known history. Their sudden appearance and the specific demands suggest a potentially opportunistic attack rather than a coordinated campaign.
Recommended Actions for Snowflake Users
Following the breach, Snowflake has provided specific guidelines to its customers on how to protect their data and strengthen their security postures. The company recommends that users enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), review IoCs, and follow security best practices.
Furthermore, by utilizing the SOCRadar XTI platform, organizations can stay ahead of cyber threats, protecting their data and reputation. With its extensive monitoring capabilities across all internet surfaces, including the often elusive dark web, SOCRadar offers Dark Web Monitoring and Dark Web News services, among its other capabilities.
Dark Web Monitoring acts as a digital periscope, delving into the dark web to detect and track the unauthorized distribution of sensitive data. With the Dark Web Monitoring module, organizations can receive immediate notifications about potential threats, enabling swift actions to mitigate risks.
By monitoring the dark web, you can maintain a vigilant watch on discussions and activities related to your organization among threat actors, ensuring you are always informed of potential vulnerabilities.
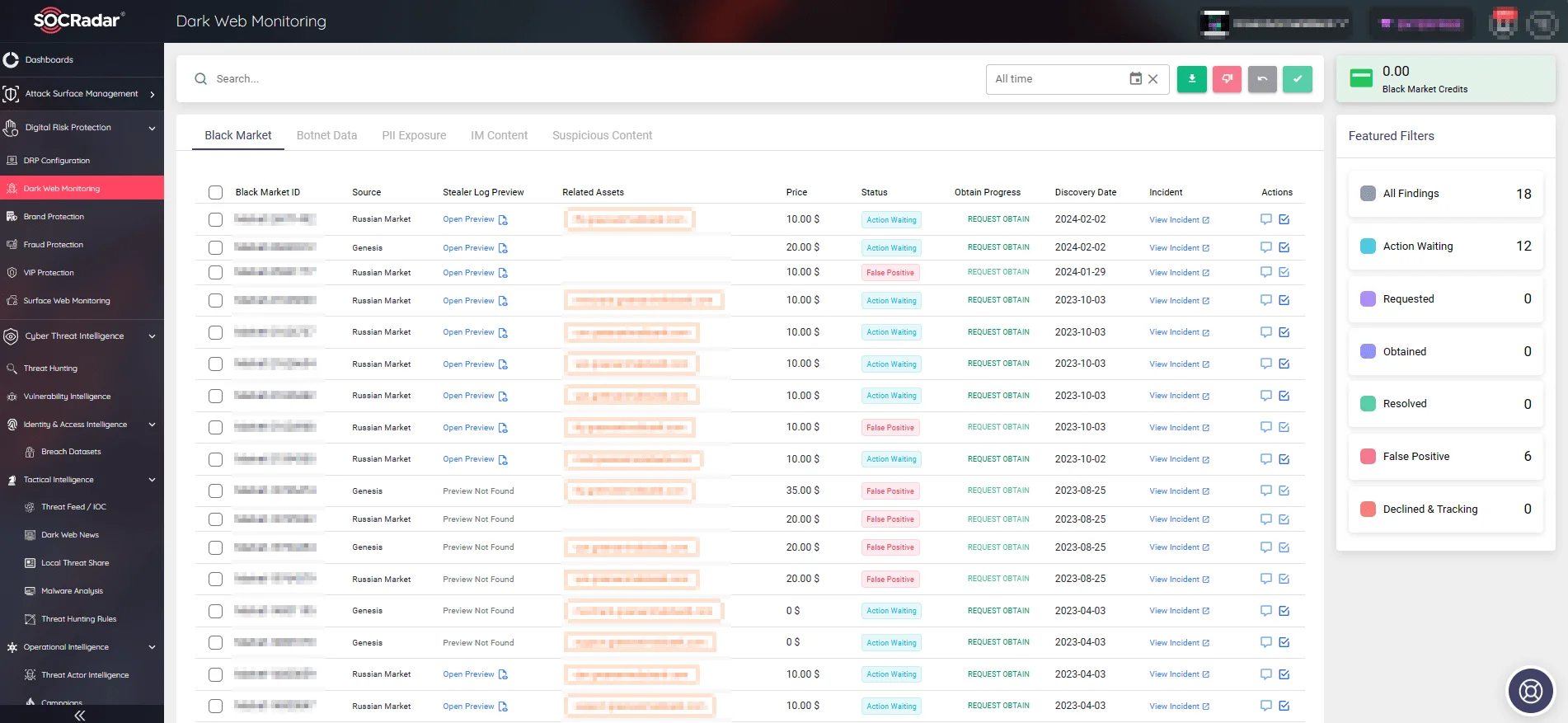
Dark Web Monitoring feature under the Digital Risk Protection module
Also, with Dark Web News, you can stay updated with the latest events and developments in the dark web landscape. The module allows viewing the latest posts through Deep and Dark Web forums, and various other hacker channels.
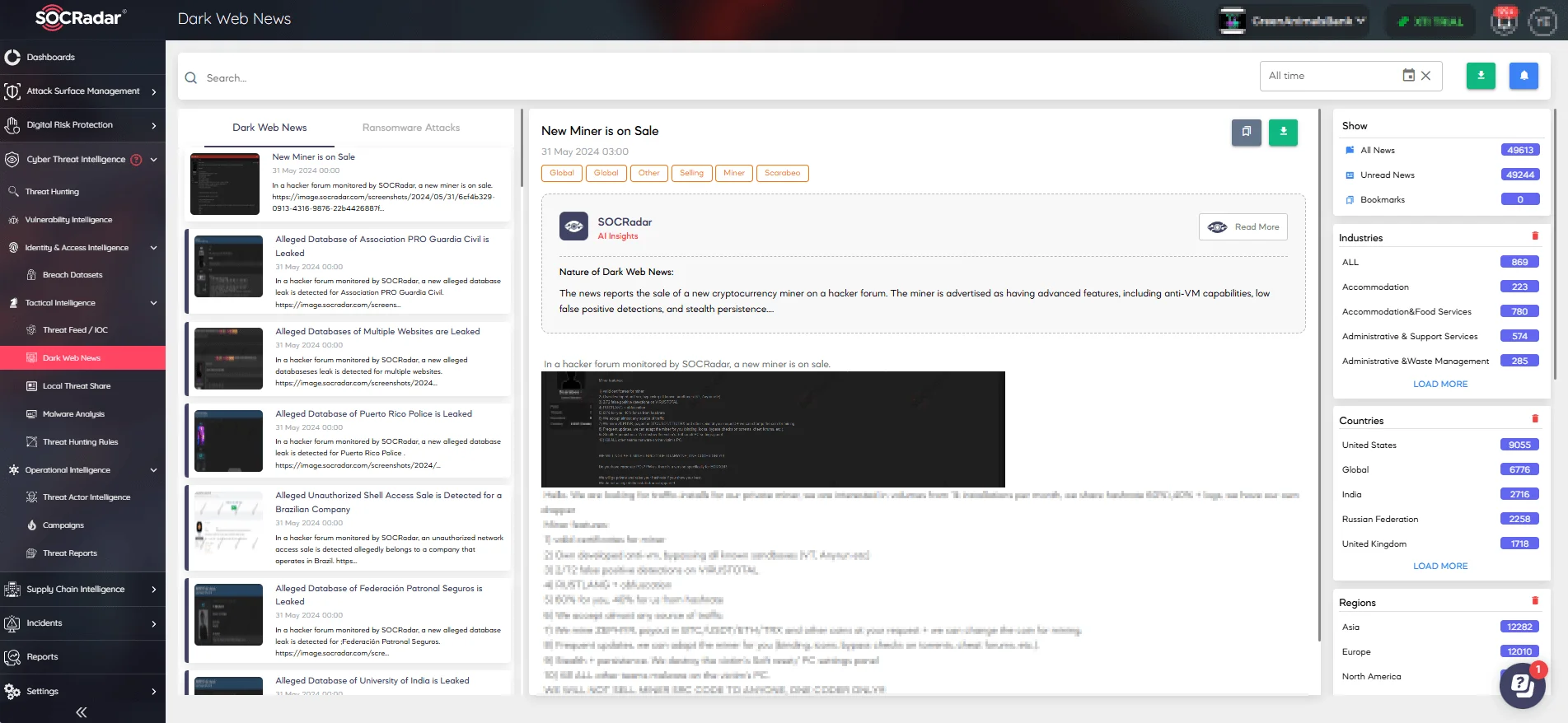
Dark Web News – Visit SOCRadar LABS to try its complementary version, DarkMirror
Article Link: Overview of the Snowflake Breach: Threat Actor Offers Data of Cloud Company’s Customers - SOCRadar® Cyber Intelligence Inc.
1 post - 1 participant
Malware Analysis, News and Indicators - Latest topics



Post a Comment
Post a Comment