Cybersecurity is a constant back-and-forth between the defenders and the threat actors, all centered around finding vulnerabilities in software. Playing a crucial role in defending against the vulnerabilities is the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). At the core of CISA’s defense strategy is the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog – a kind of superhero toolkit for digital security.
Think of the CISA KEV catalog like a vigilant guard, keeping a detailed record of software weak spots that are under active exploitation. It is not just a list; it is a go-to resource for governments, businesses, and individuals dealing with the complexities of cybersecurity. This organized catalog sorts vulnerabilities by vendor, product, date, and description, offering not only a heads-up but also practical advice on how to tackle these risks.
For those familiar with the ins and outs of cybersecurity, the KEV catalog is like a handy guide, pinpointing the exact vulnerabilities that crafty threat actors exploit. It is not just about spotting weaknesses; it is a roadmap for strengthening our defenses.
With this 2023 review of the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, we delve into the latest trends of exploited vulnerabilities, unraveling the threads that connect the past, present, and future cybersecurity challenges.
What is the Benefit of the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog?
The Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog emerges not just as a repository but as a strategic asset, designed to empower the cybersecurity community and enhance the resilience of organizations against evolving threat activities.
- Prioritized Defense Strategies:
Aligned with this mission, CISA actively curates the KEV list, focusing on vulnerabilities that have witnessed active exploitation. By setting due dates for organizations to patch specific vulnerabilities identified in the catalog, CISA underscores the critical importance of timely remediation. This strategic approach encourages organizations to prioritize actions that not only safeguard their individual systems but contribute to the collective resilience of the cybersecurity community.
- Proactive Resilience Against Ransomware:
A noteworthy facet of the KEV catalog is its role in the identification and cataloging of vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware groups. Beyond merely reacting to threats, CISA’s proactive stance enables organizations to fortify their digital environments.
In a recent enhancement, CISA introduced the “Known to be Used in Ransomware Campaigns” column to the KEV list. Armed with insights from the catalog, organizations can streamline patching efforts, reinforce security protocols, and enhance incident response strategies. The result is a tangible reduction in the risk of falling victim to ransomware attacks.
- Strengthened Collaboration and Information Sharing:
CISA fosters a culture of collaboration by encouraging organizations and individuals to contribute to the KEV catalog. They actively seek information about exploited vulnerabilities not currently listed, recognizing the value of shared intelligence in fortifying the entire cybersecurity ecosystem.
As we explore the benefits of the KEV catalog, it becomes evident that it is not just a static list but a dynamic resource that actively contributes to the proactive defense and collective strength of the cybersecurity community.
Yearly Statistics Regarding the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog – 2023
As of November 2023, CISA KEV boasts 1,041 meticulously cataloged vulnerabilities. Let’s delve into the data, parsing through the numbers to discern insights regarding the dynamics of the exploited vulnerabilities.
To gain a more nuanced understanding, we have scrutinized the data based on several key parameters: year of inclusion, CVE years, vendor origin, vulnerability types, and ransomware exploitation. This multifaceted analysis provides a comprehensive view of the evolving nature of threats and the systems they target.
How Many Vulnerabilities Have Been Added to the KEV Catalog in 2023?
In the ongoing year of 2023, the CISA KEV catalog has welcomed 174 new vulnerabilities into its fold. It is crucial to note that the year is still in progress, and this tally is not final. Comparing this figure to the preceding year, there appears to be a notable decrease. In 2022, the catalog experienced a surge with over 500 new vulnerabilities added.
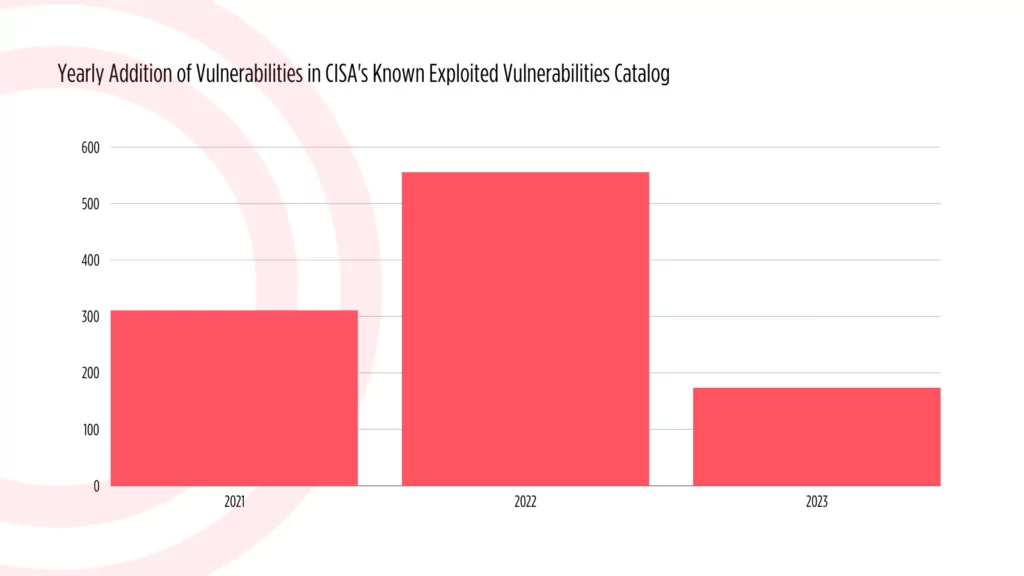 Yearly addition of vulnerabilities in CISA’s KEV Catalog
Yearly addition of vulnerabilities in CISA’s KEV Catalog
CVEs According to the Years
In 2023, although the overall count of added vulnerabilities is lower, a substantial portion of the entries bears recently assigned Common Vulnerability and Exposure (CVE) identifiers. Contrastingly, the statistics from 2022 reveal that many of the vulnerabilities added have older CVE identifiers.
Below are the statistics for all CVEs included in the KEV catalog, organized according to the years in which they were identified:
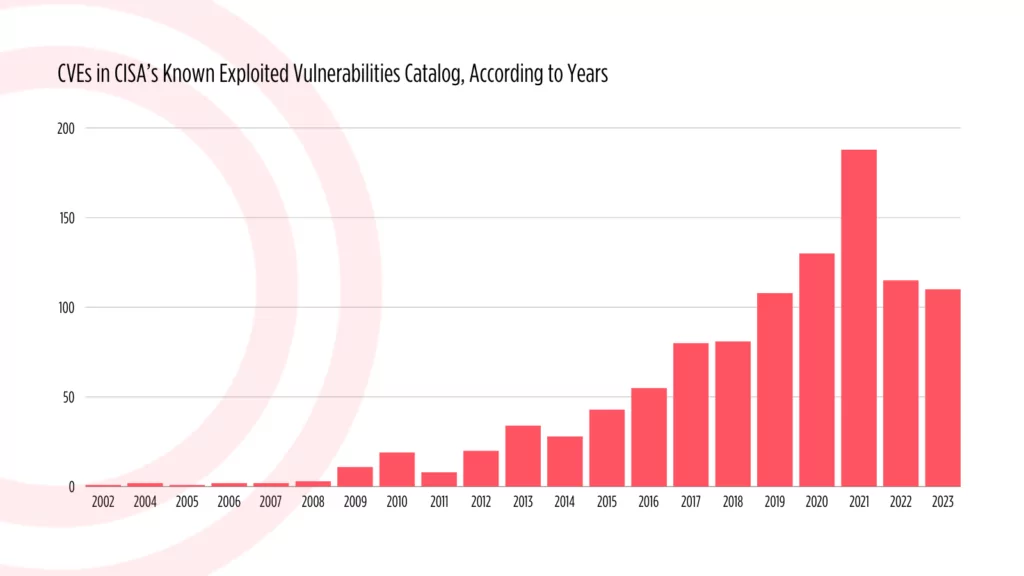 CVEs in CISA’s KEV catalog, according to years
CVEs in CISA’s KEV catalog, according to years
Top Vendors on the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog for 2023
This year, Microsoft continues to hold the top position in the CISA KEV catalog, featuring prominently both in terms of exploited vulnerabilities and on the radar of threat actors. In 2022, Microsoft claimed a substantial 27.4% among other vendors, but this year, the figure has shifted to 15.5%.
Following closely, Apple has the second spot as a frequently targeted vendor, holding a 10.9% share, followed by tech giant Samsung and networking leader Cisco. Below is a breakdown of the top 10 vendors whose products faced vulnerabilities leading to inclusion in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) list in 2023.
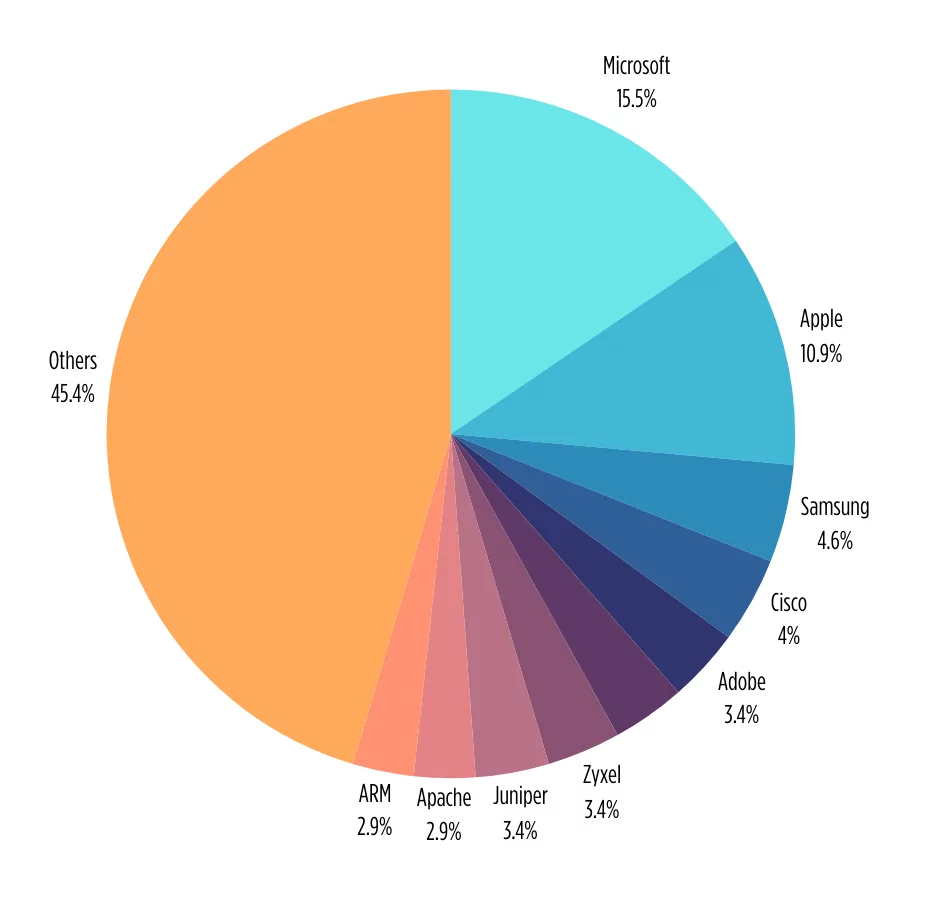 Top vendors with exploited vulnerabilities in CISA KEV 2023
Top vendors with exploited vulnerabilities in CISA KEV 2023
What Are the Top Vulnerability Types Added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog in 2023?
Examining the data on the primary vulnerability types and their respective percentages in the CISA KEV catalog underscores the critical role of specific vulnerability types in the realm of cybersecurity.
Surprisingly, 2023 reveals a notable shift in threat actor behavior and exploitation trends. Privilege escalation vulnerabilities take the lead with 12.1% in CISA KEV 2023.
In the previous year, Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilities overwhelmingly dominated the CISA KEV list, but in the current landscape of 2023, privilege escalation emerges as the top vulnerability. Following closely, RCE claims the second position, with vulnerabilities categorized as “Command Injection” securing the third spot in the hierarchy. This dynamic shift in vulnerability types emphasizes the ever-changing nature of cybersecurity challenges and the need for adaptive defense strategies.
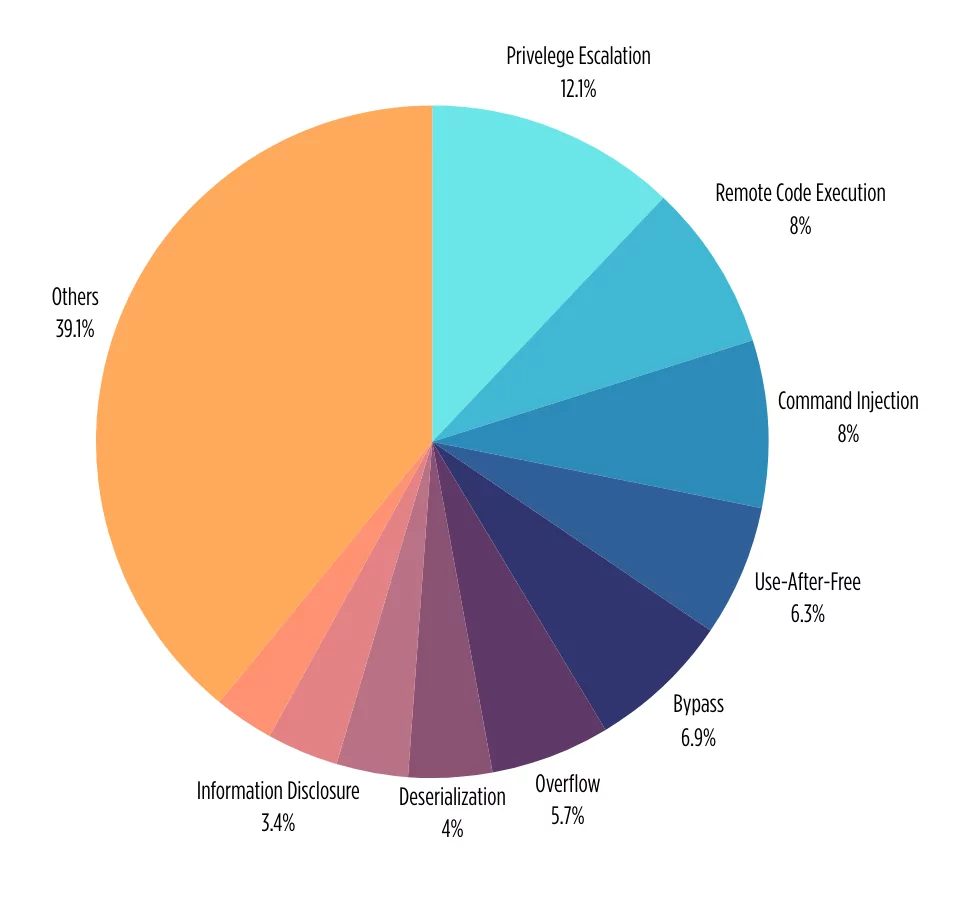 Top vulnerabilities in CISA KEV 2023
Top vulnerabilities in CISA KEV 2023
How Many Vulnerabilities Have Been Targeted by Ransomware Threat Actors?
The CISA KEV catalog not only identifies known vulnerabilities but also reveals if they have connections to ransomware campaigns.
In a pivotal step forward, CISA has recently bolstered its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog with a groundbreaking addition – a label identifying vulnerabilities “known to be used in ransomware campaigns.” This strategic enhancement delivers invaluable insights, shining a spotlight on vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware groups. It empowers organizations to actively prioritize their patching efforts, reinforcing their digital defenses against the relentless rise of ransomware threats.
Below are the statistics regarding vulnerabilities tagged as “known to be used in ransomware campaigns” by CISA. In 2023, ransomware actors exploited approximately 13.7% of vulnerabilities added to the CISA KEV catalog.
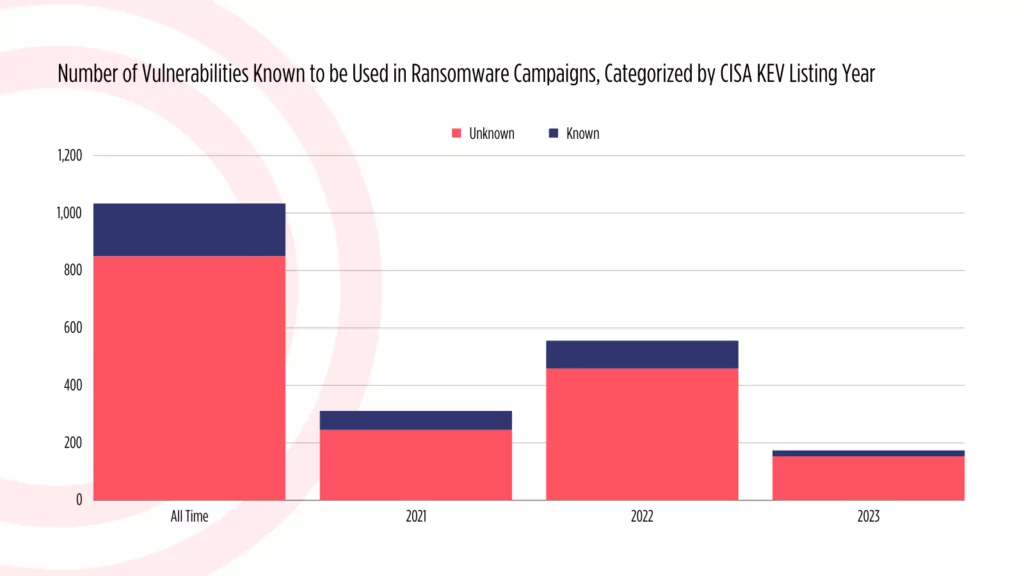 CISA KEV vulnerabilities used in ransomware campaigns
CISA KEV vulnerabilities used in ransomware campaigns
SOCRadar ASM – Ransomware Check Feature
Complementing this proactive stance, the SOCRadar platform has previously introduced its own feature called “Ransomware Check”. Its functionality mirrors CISA’s recent enhancement in the KEV catalog. When you search for a vulnerability on the SOCRadar platform, through the Attack Surface Management module, you can gain insights into whether it has been targeted by ransomware operations.
The feature can allow you to assess the potential impact on your organizational digital assets and access pertinent information, reinforcing a comprehensive approach to safeguarding against ransomware threats.
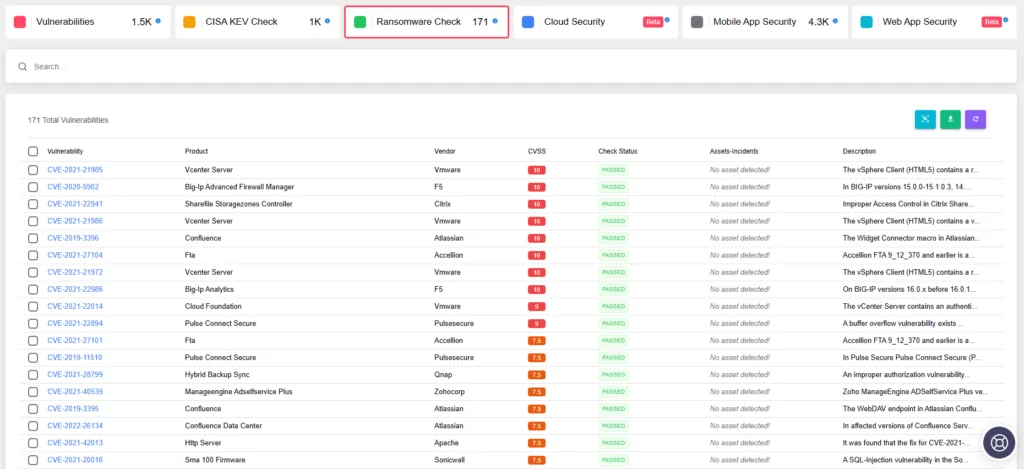 SOCRadar ASM/Company Vulnerabilities, Ransomware Check
SOCRadar ASM/Company Vulnerabilities, Ransomware Check
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management module fortifies an organization’s defenses by delivering real-time alerts about vulnerabilities that directly affect its digital assets. This proactive feature guarantees that organizations stay abreast of the latest information concerning these vulnerabilities and their potential impact. This capability becomes particularly crucial, when threat actors’ activity regarding a vulnerability is on the rise, enabling organizations to swiftly safeguard against potential exploitation. With SOCRadar, organizations are equipped with the tools and insights necessary to navigate and mitigate emerging threats, ensuring a robust and resilient cybersecurity posture.
What are the Latest Vulnerabilities in the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog in 2023?
CVE-2023-29552 (CVSS score: 8.6)
SLP (Service Location Protocol), a service discovery protocol enabling devices to find services in local networks, has been identified as vulnerable, potentially leading to amplification attacks.
The vulnerability was found to be affecting over 2,000 global organizations and 54,000 SLP instances accessible via the internet, including VMWare ESXi Hypervisor, Konica Minolta printers, Planex Routers, IBM Integrated Management Module (IMM), SMC IPMI, and 665 other products.
CVE-2023-29552 could be exploited for massive volumetric Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks, with the potential for amplification up to 2,200 times.
CISA added this vulnerability to the KEV catalog on November 8, 2023.
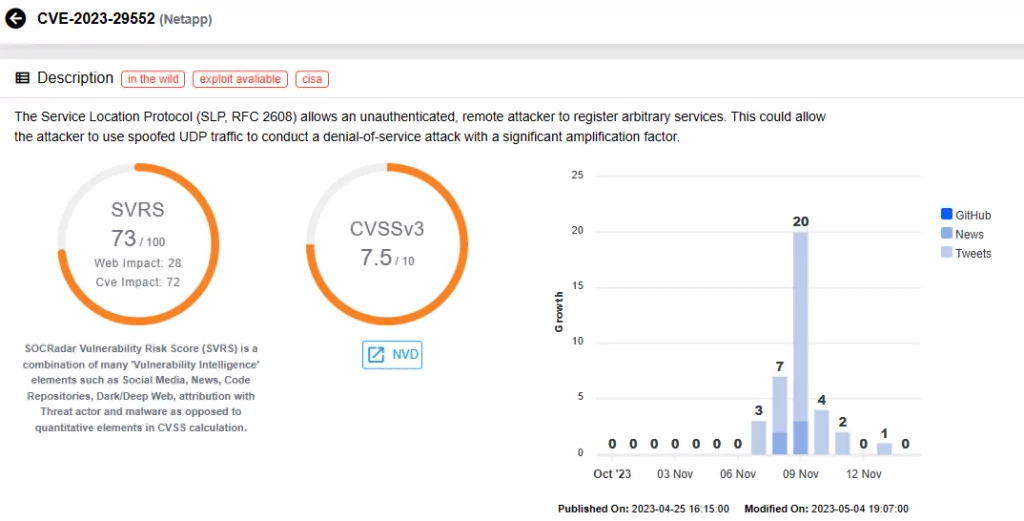 Vulnerability card for CVE-2023-29552 (SOCRadar)
Vulnerability card for CVE-2023-29552 (SOCRadar)
CVE-2023-22518 (CVSS score: 9.8)
CVE-2023-22518, a critical Improper Authorization Vulnerability, poses significant data loss risks in Confluence Data Center and Server. Researchers discovered attempts to exploit this vulnerability in Windows and Linux systems; some of these attempts, observed since November 5, involved Cerber Ransomware’s deployment.
Researchers have hinted at the possibility of widespread exploitation targeting vulnerable Confluence servers. Atlassian CISO has made an announcement, emphasizing the importance of addressing this critical vulnerability promptly.
The CVE-2023-22518 vulnerability was added to the CISA KEV catalog on November 7, 2023.
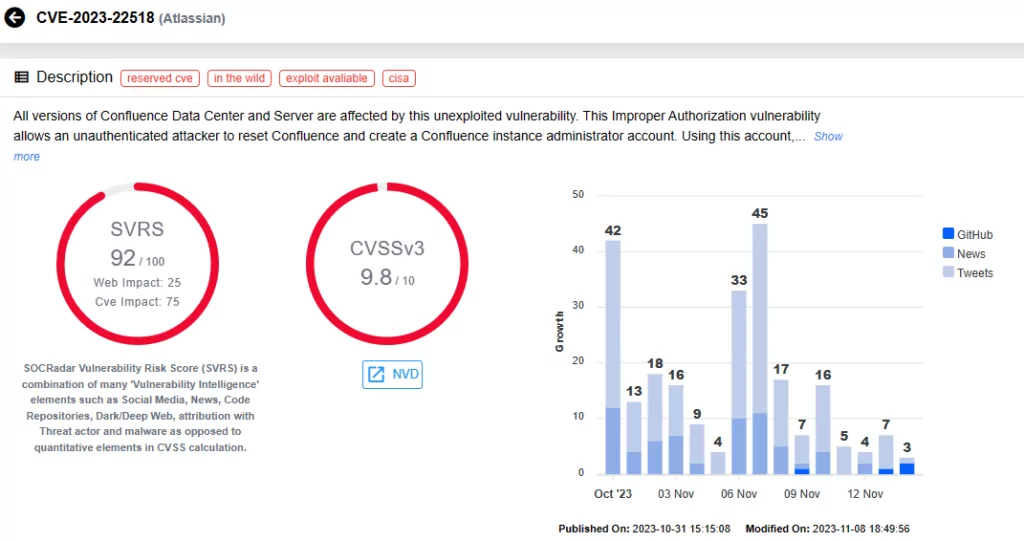 Vulnerability card for CVE-2023-22518 (SOCRadar)
Vulnerability card for CVE-2023-22518 (SOCRadar)
CVE-2023-46604 (CVSS score: 9.8)
A recently disclosed security vulnerability in Apache ActiveMQ, CVE-2023-46604, has prompted serious concerns. With a critical CVSS score of 9.8, this vulnerability poses a significant risk of remote code execution (RCE) attacks.
Threat actors exploited CVE-2023-46604 to deploy the HelloKitty Ransomware, late on, it was also leveraged for deploying the TellYouThePass Ransomware. Notably, since at least October 10, 2023, CVE-2023-46604 has been exploited as a zero-day vulnerability to deploy SparkRAT, a cross-platform remote access trojan (RAT).
CISA added this critical vulnerability to the KEV catalog on November 2, 2023.
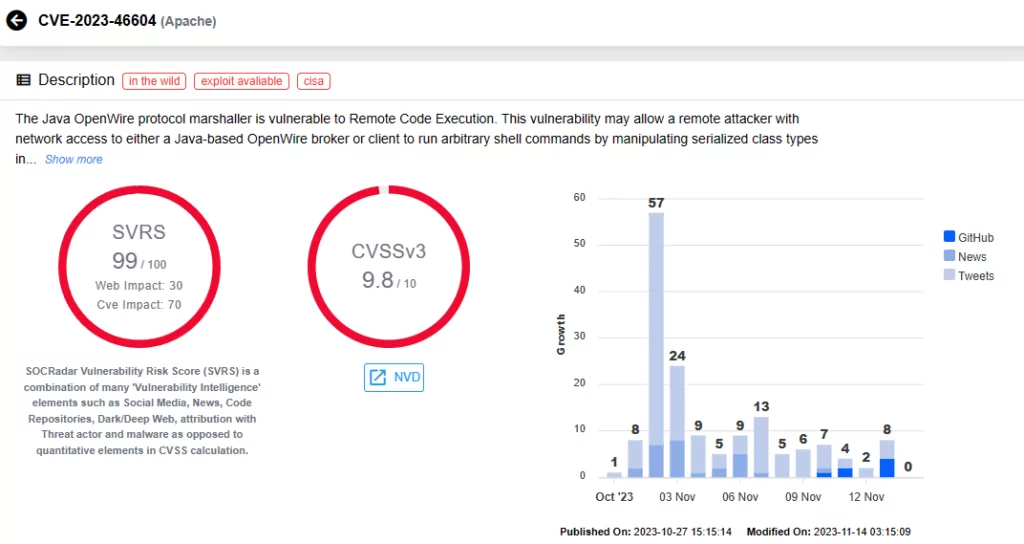 Vulnerability card for CVE-2023-46604 (SOCRadar)
Vulnerability card for CVE-2023-46604 (SOCRadar)
CVE-2023-46747 & CVE-2023-46748 (CVSS scores: 9.8, 8.8)
A critical vulnerability, CVE-2023-46747, was recently discovered in F5 BIG-IP products, allowing unauthenticated remote code execution. This vulnerability holds a critical severity, raising substantial security concerns.
F5’s recent advisory update reports active exploitation activity for this vulnerability; it is further noted that CVE-2023-46747 has been used in combination with CVE-2023-46748 in attacks.
CISA has added the two vulnerabilities to the KEV catalog on October 31, 2023.
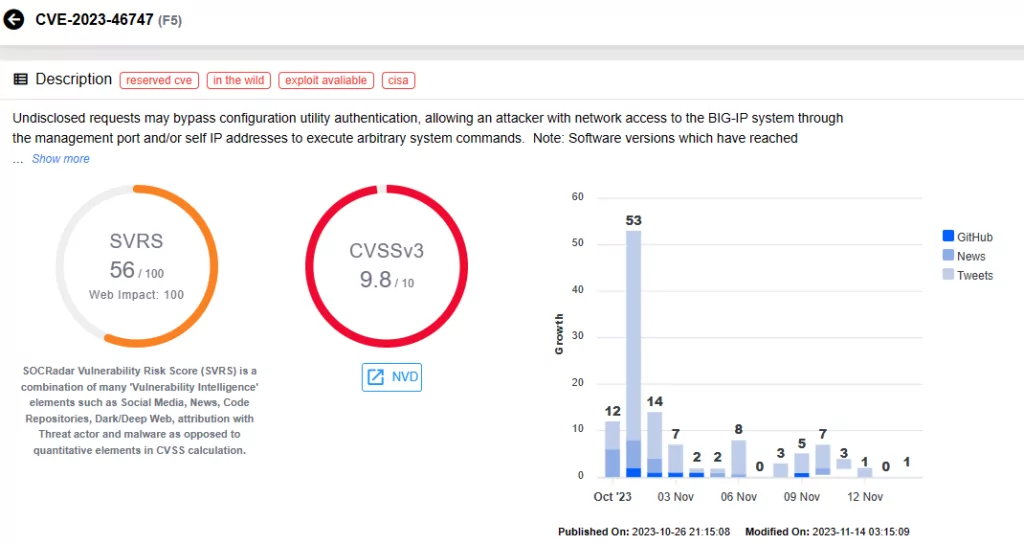 Vulnerability card for CVE-2023-46747 (SOCRadar)
Vulnerability card for CVE-2023-46747 (SOCRadar)
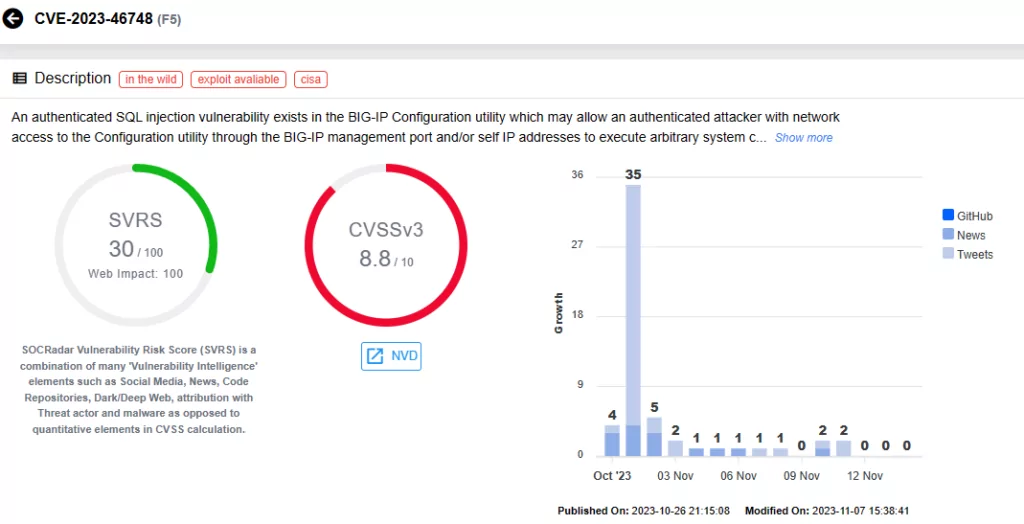 Vulnerability card for CVE-2023-46748 (SOCRadar)
Vulnerability card for CVE-2023-46748 (SOCRadar)
Within the ASM module, alongside the Ransomware Check feature, there is also a CISA KEV Checkfeature, providing you with the ability to ascertain if any vulnerabilities affecting your assets have been incorporated into the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog by CISA.
Compliant organizations must update CISA on their progress while they are addressing the vulnerabilities listed in the KEV catalog, because failure to adhere to the vulnerabilities’ due dates may result in penalties and even loss of contracts. This is why the CISA KEV Check feature on SOCRadar is valuable, notifying organizations about potential issues that threaten their compliance.
Further explore SOCRadar’s capabilities in Vulnerability Intelligence with CVE Radar, a complimentary feature from SOCRadar Labs. CVE Radar enables you to track vulnerability trends seamlessly, offering clarity on the most frequently mentioned vulnerabilities, associated exploits, repositories, and the latest updates conveyed through tweets and news blogs.
Conclusion
The KEV catalog serves as a superhero toolkit for digital security, offering more than a mere repository—it’s a strategic asset empowering the cybersecurity community. From prioritized defense strategies to proactive resilience against ransomware, the catalog’s impact is multi-faceted.
The 2023 review of the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog provides a strategic glimpse into the trends in vulnerability exploitation. Anchored by the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), this review navigates the complexities of exploited vulnerabilities.
Yearly statistics offer insights, revealing a notable decrease in vulnerabilities added in 2023. Microsoft continues to hold the top position in the CISA KEV catalog, featuring prominently in terms of exploited vulnerabilities and on the radar of threat actors. The catalog’s connection to ransomware campaigns is clear, with approximately 13% of vulnerabilities added in 2023 having been exploited in ransomware operations.
Beyond the numbers, the CISA KEV catalog represents a dynamic resource actively contributing to the proactive defense and collective strength of the cybersecurity community. As organizations navigate the intricacies of the digital world, this review can serve as a guide, offering insights into the threat actors’ latest points of interest.
Exploring the latest vulnerabilities, such as CVE-2023-29552 and CVE-2023-22518, reveals the need for proactive defense measures; CISA’s strategic enhancements and SOCRadar’s capabilities offer a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity, fortifying defenses against potential threats.
The post 2023 Review of the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog appeared first on SOCRadar® Cyber Intelligence Inc..
Article Link: 2023 Review of the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog
1 post - 1 participant
Malware Analysis, News and Indicators - Latest topics



Post a Comment
Post a Comment